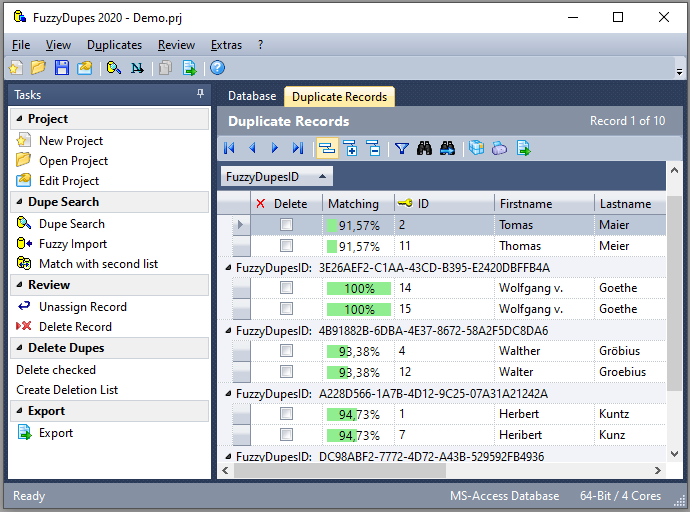
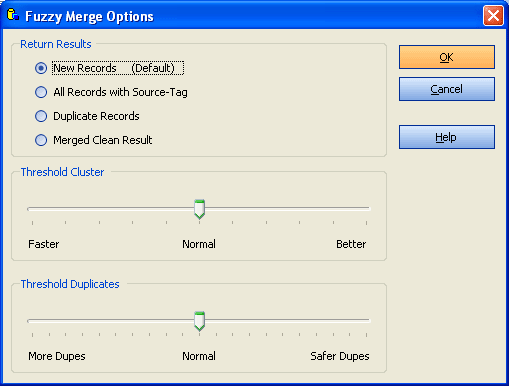
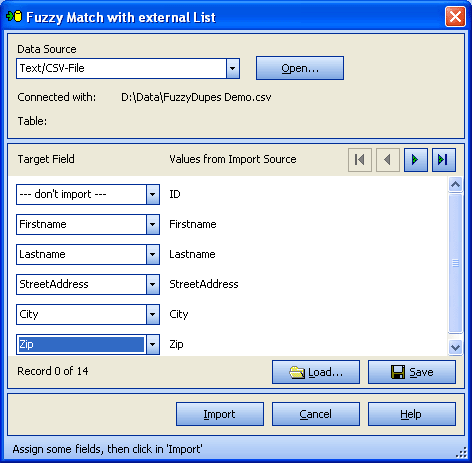
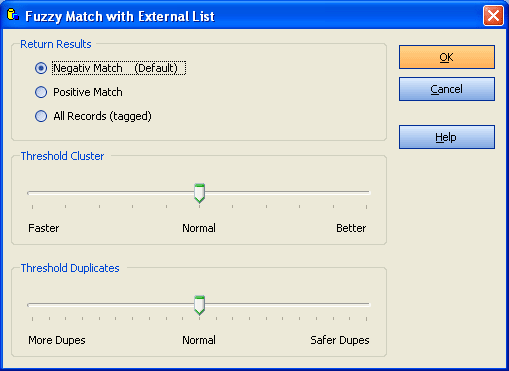
Project Wizard
Select in main menu "File->New Project".
This launches the Project Wizard.
Database Connection
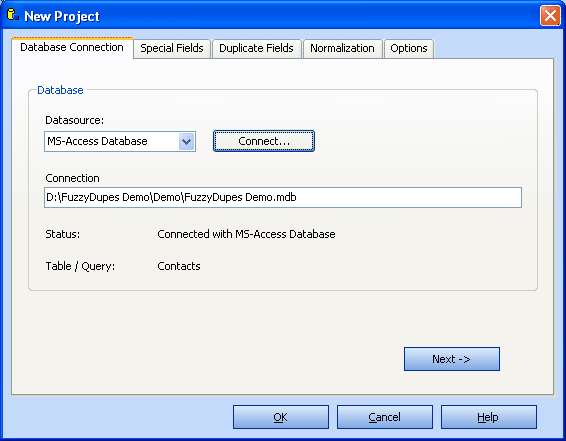
Select one of the following data sources:
- MS-Access Database
- MS SQL-Server Database
- MS-Excel Workbook
- Text file with delimiter (CSV files)
- MS-Outlook Contact Folder
- Windows Addressbook
- SharePoint Server
- BulkMailer Addresses Database
- Other (Datalink Dialog)
Click on Connect to continue. More options follow, depending on the selected data source.
You can connect to all databases that come with an ODBC driver or OLEdb-Provider, e.g. Oracle, MySQL and many more.
- Download and install the ODBC-driver from the databases manufacturers website.
- Use the ODBC-Manager to create a System Data Source.
- In this dialog, select "Other (Datalink Dialog)"
- Connect to your database
- In the Datalink Dialog check Save Password, so that the application has further access to the database.
Subsequently select the Table or View/Query, which contains the data.
Then click on "Next".
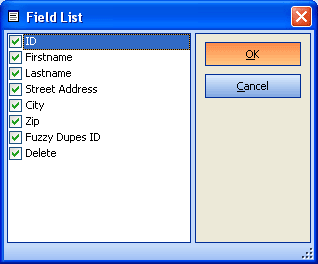
Special Fields
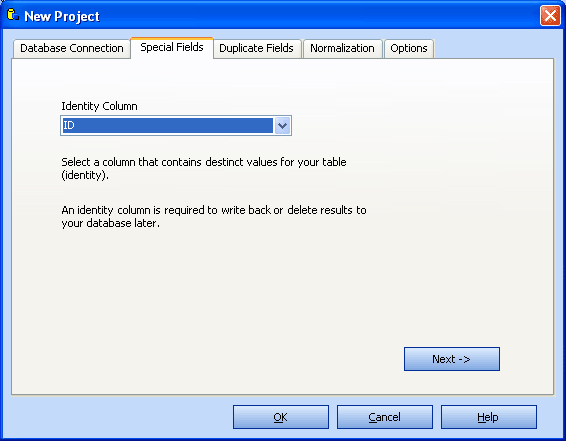
Choose a column from your table which contains distinct values (identity column).
This column should also contain a primary key.
Duplicate Fields
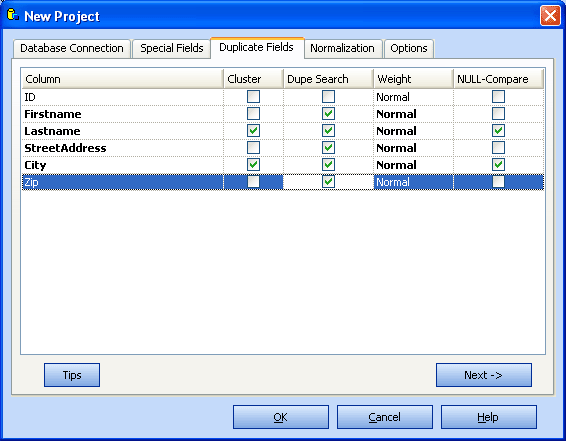
Select 2-4 columns for cluster creation.
These columns should be filled with data very well.
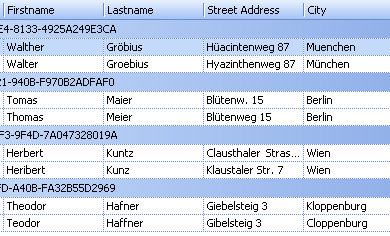
Only select columns of type character/string. ZIP-codes are unsuitable for cluster creation. With address data select e.g. LastName, Street, City
Select some columns for the duplicate search.
Select at last all columns, that are marked for cluster creation, and some more.
With address data you typically select
- LastName
- FirstName
- (Company)
- ZIP
- Street Address
- City
- [Phone]
- [..]
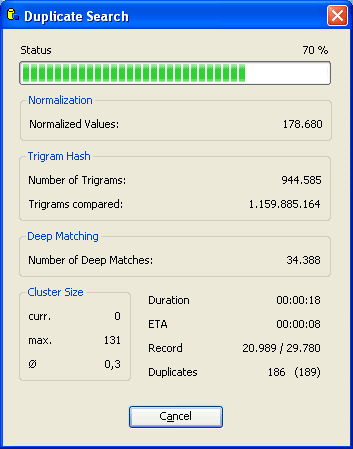
Using fuzzy comparison algorithms, the program will calculate the correspondence
in each of the selected fields. The program then uses these results to calculate
the average correspondence between two records.
Most of the time, leave all quantifiers on Normal.
If you want, you can place more or less emphasis on an individual column.
Select Identical, if exact correspondence is required for a particular column.
The "Identical" option is especially useful with grouped data sets,
although duplicates can then only appear within defined groups.
Select Identical for the group column.
Select NULL Comparison for columns that contain values in (nearly) all rows
(e.g. Last Name, Street, ZIP, City).
For other columns which may contain NULLs in many rows don't select NULL Comparison
(e.g. First Name, Phone, Fax, ...)
With NULL Comparison, empty values (NULL-Values) are used for the
calculation of the average correspondence between two records.
Click on "Next" to continue.
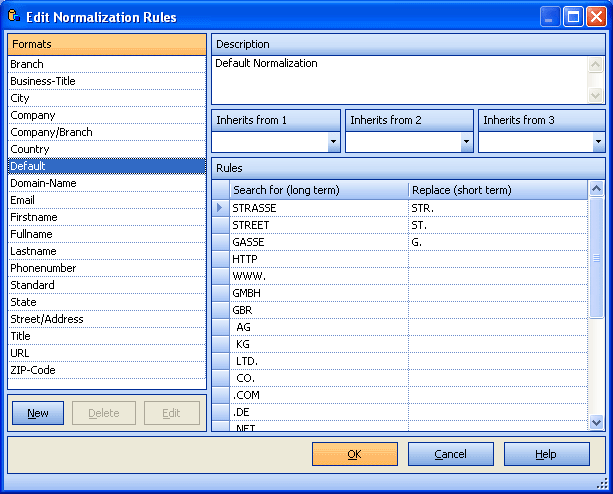
Normaization
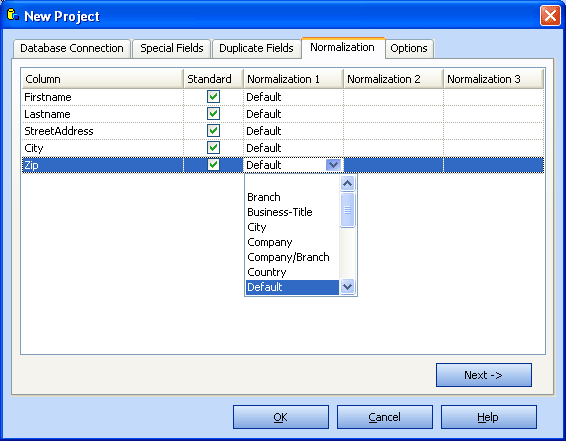
Standard normalization converts all characters to uppercase, replaces special characters and umlauts etc. Standard normalization should usually checked for all columns.
Select up to 3 different normalization rules for each column.
Use "default" on address data when you're not sure and when you don't have user defined normalization rules.
Use the Normalization Rules Editor to customize rules or add new rules.
Options
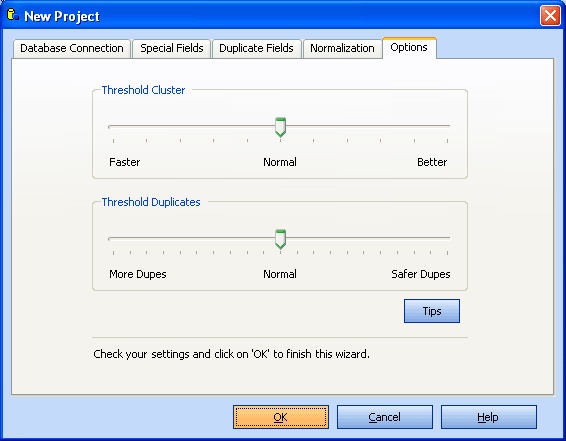
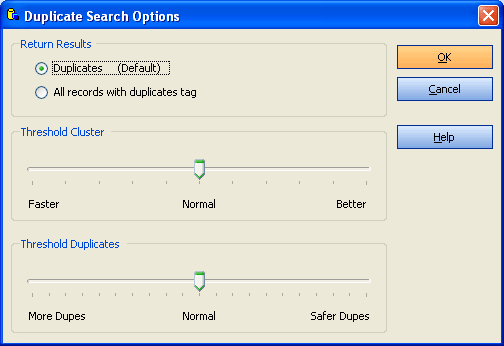
With this slider you can influence the cluster size.
In most cases you will leave this at normal position.
It is not a good idea to set it to the most right position, because this will only slow down the search but gives no better results.
With large databases, you may want to set it a little bit to "faster" to speed up the search.
This setting has the most relevant effect on the search results.
Default is 90. Later you can repeat the duplicate search with a different
threshold value. Increase this value if too many duplicates were found.
Choose a lower value if not enough duplicates were found.
Check your settings and click on "OK", to complete this wizard.